Contracts for Difference (CFDs) have become increasingly popular among traders seeking exposure to various financial markets without owning the underlying asset. In essence, a CFD is a contract between a trader and a broker to exchange the difference in the value of an asset from the time the contract is opened to when it is closed. Here’s what you need to know about CFD how it works:
1. How CFDs Work:
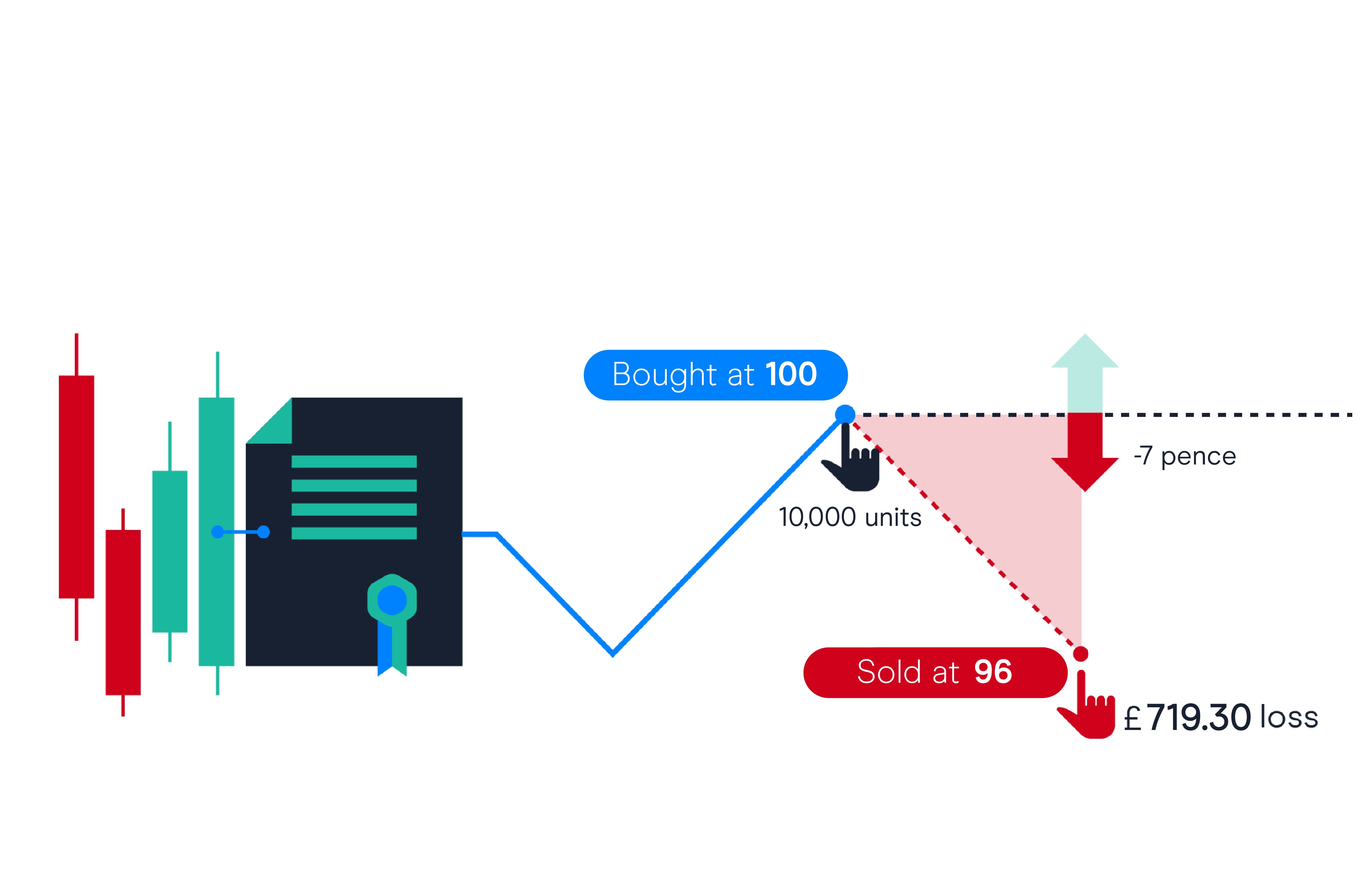
CFDs allow traders to speculate on the price movements of assets such as stocks, commodities, currencies, and indices without owning them. When you trade CFDs, you are essentially betting on whether the price of the asset will rise or fall. If your prediction is correct, you profit; if it’s wrong, you incur a loss.
2. Flexibility in Leverage:
CFD trading offers flexible leverage, allowing traders to amplify their positions with borrowed funds. This means that you can control a larger position size with a smaller initial investment. However, it’s crucial to understand that while leverage can magnify profits, it also increases the risk of losses.
3. Diverse Asset Classes:
One of the key attractions of CFDs is their versatility. Traders can access a wide range of asset classes, including stocks, commodities, currencies, and indices, all from a single trading account. This diversity enables traders to capitalize on various market opportunities across different sectors.
4. No Ownership of Underlying Assets:
Unlike traditional investing, where you physically own the asset, CFD trading is purely speculative. You don’t own the underlying asset; instead, you are entering into a contract with your broker to settle the difference in price between the opening and closing of the trade.
5. Potential for Profits and Losses:
CFD trading offers the potential for both substantial profits and losses. Since CFDs are leveraged products, even small price movements can result in significant gains or losses. It’s essential for traders to implement risk management strategies, such as setting stop-loss orders, to mitigate potential losses.
6. Trading Opportunities in Both Rising and Falling Markets:
Another advantage of CFDs is that they allow traders to profit from both rising and falling markets. If you believe that the price of an asset will increase, you can open a long (buy) position. Conversely, if you anticipate a price decline, you can open a short (sell) position.
In conclusion, CFDs are versatile financial instruments that offer traders the opportunity to speculate on the price movements of various asset classes with flexible leverage. However, it’s crucial for traders to fully understand the risks involved and to trade responsibly.
